Description
Overview
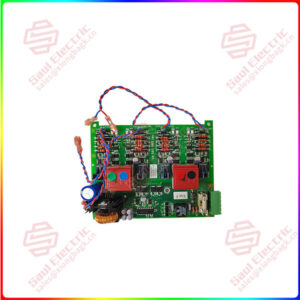
Essential details:CLSR-33-N2CE-1 Linear motor controller
lf you need to inquire or purchase ,please send the product models to my email or call medirectly .
sunny He
[Email] sales@saulcontrol.com
[Mobile] 86-18059884797
[WhatsApp] 86-18059884797
[Skype] sales@saulcontrol.com
CLSR-33-N2CE-1 Linear motor controller
The working principle of linear motor controller mainly involves the precise control of linear motor. Here’s a detailed explanation of how it works:
Power and signal conversion: The linear motor controller first receives the external power signal and converts it into the specific signal required for the linear motor drive. These signals may include switching signals, PWM (pulse width modulation) signals, etc., to meet the working requirements of linear motors.
Driver output control: The controller realizes accurate control of the output of the linear motor driver by adjusting parameters such as current, voltage and frequency. This control can cover a number of aspects, such as positioning, motion, acceleration and deceleration functions, to ensure that the linear motor can operate in a predetermined manner.
Monitoring and feedback information: The linear motor controller is not only responsible for sending control signals, but also has real-time monitoring and feedback functions. It can sense the motion state, position, speed and load of the linear motor itself, and feed this information back to the control system. This feedback mechanism helps to achieve precise control of the motor and ensure the stability and reliability of its operating state.
Automatic control integration: Through the connection with external control equipment (such as PLC, HMI, PC, etc.), the linear motor controller can realize the automatic control and integration of the entire production line. This means that it can work in tandem with other automation equipment and systems to enable more efficient and precise automated production processes.
In summary, the working principle of linear motor controller involves many aspects such as power and signal conversion, driver output control, monitoring and feedback information, and automation control integration. Together, these functions ensure that the linear motor can operate precisely according to predetermined requirements to meet the needs of a variety of automated production scenarios.


 1 Year Warranty
1 Year Warranty