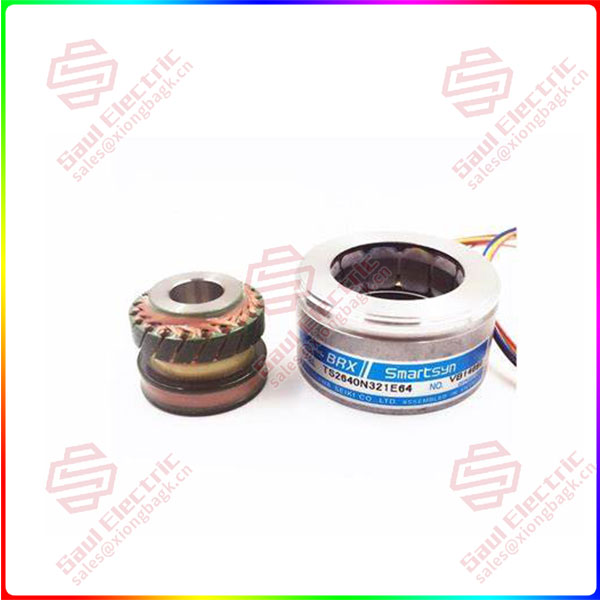
Position sensor (Hall sensor)
Since there are no brushes in the BLDC motor, the commutation is electronically controlled. In order for the motor to rotate, the stator windings must be energized sequentially, and the position of the rotor (i.e., the north and south poles of the rotor) must be known to precisely energizing a specific set of stator windings.
A position sensor with a Hall sensor (operating on the principle of the Hall effect) is usually used to detect the position of the rotor and convert it into an electrical signal. Most BLDC motors use three Hall sensors, which are embedded in the stator to detect the position of the rotor.
The output of the Hall sensor will be high or low, depending on whether the North Pole of the rotor is South or near the North Pole. By combining the results of the three sensors, the exact sequence of power-on can be determined.


 1 Year Warranty
1 Year Warranty